Read More:
Distribution of Genetically Modified Mosquitoes to Combat Dengue Fever in Brazil
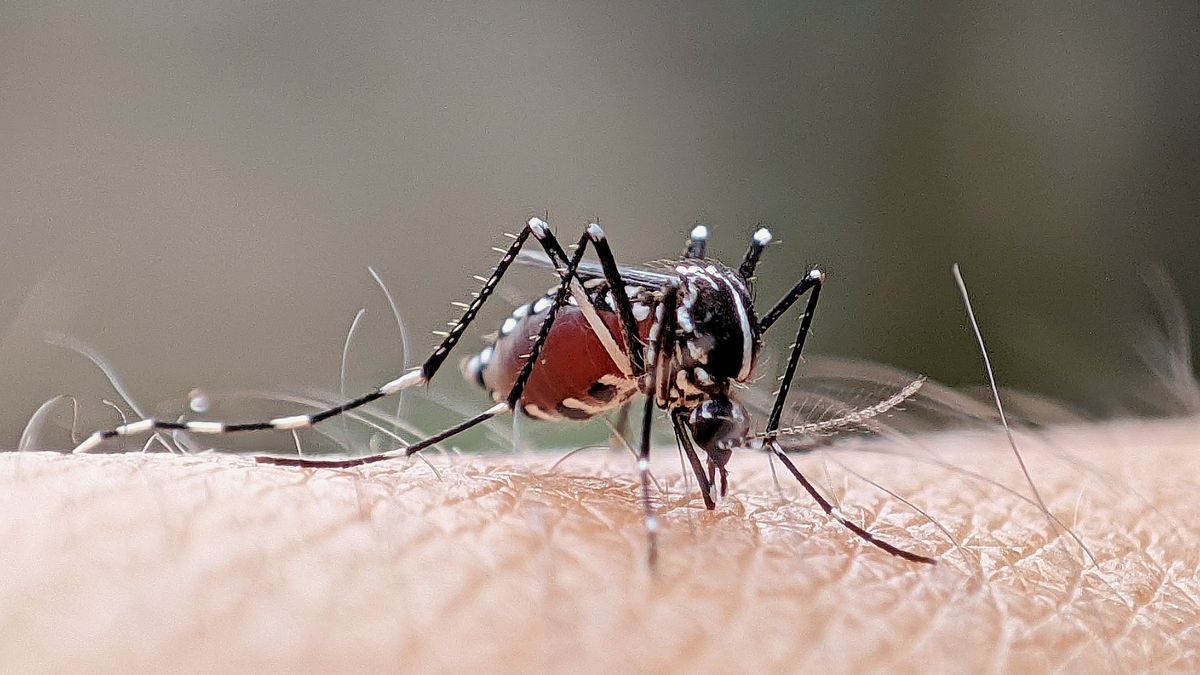
Scientists have recently announced the release of genetically modified mosquitoes in Brazil as part of an innovative strategy to combat the spread of dengue fever. These mosquitoes have been specially engineered to help reduce the population of disease-carrying mosquitoes in the region.
Implementation of Cutting-Edge Technology in Disease Control Efforts
The use of genetically modified mosquitoes represents a significant advancement in disease control efforts. By releasing these modified insects into the wild, researchers hope to suppress the population of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes, which are known vectors of dengue fever. This approach could potentially help reduce the incidence of this debilitating disease in the community.
Positive Results from Previous Trials
Previous trials of genetically modified mosquitoes have shown promising results. In areas where these modified insects were released, there was a significant decrease in the population of disease-carrying mosquitoes. This offers hope for similar success in Brazil, where dengue fever is a major public health concern.
Collaboration between Scientists and Local Authorities
The distribution of genetically modified mosquitoes is a collaborative effort between scientists and local authorities in Brazil. By working together, these stakeholders hope to effectively control the spread of dengue fever and protect the health of residents in the region. This partnership is crucial in ensuring the success of this innovative disease control strategy.
Future Outlook for Dengue Control Efforts
With the distribution of genetically modified mosquitoes in Brazil, there is renewed optimism in the fight against dengue fever. Scientists believe that this approach could help reduce the burden of this disease on the community and lead to improved public health outcomes. Continued monitoring and research will be key in assessing the long-term impact of this innovative strategy.
Read More:
- Sweeping public safety bill in D.C. aims to increase security, undoing past changes
- Get Ready for Enchanting Adventures in Season 4 with Witch Doctor
- Talk therapy shown to be effective in addressing psychological factors contributing to back pain
- Microsoft eliminates Android app integration on Windows 11
- Seven Years Later: Racing Game Enjoys Explosive Success on Steam Thanks to Epic Sale















+ There are no comments
Add yours